This Course Is Only Available To Our Members
Short selling allows traders to profit off an asset’s price decline. It’s a very common way to manage downside risk, hedge existing holdings, or simply express a bearish outlook on the market.
However, shorting can be an exceptionally high-risk trading strategy at times. Not only because there is no upper limit for the price of an asset, but also due to short squeezes. A short squeeze can be described as a sudden price increase. When it occurs, many short sellers get “trapped” and quickly rush to the exit to try and cover their positions.
Naturally, if you’d like to understand what a short squeeze is, you’ll need to understand what shorting is first. In this article, we’ll discuss what a short squeeze is, how you can prepare for it, and even profit off it in a long position.
What is a short squeeze?
A short squeeze happens when the price of an asset sharply increases due to a lot of short sellers being forced out of their positions.
Short sellers are betting that the price of an asset will decline. If the price rises instead, short positions start to amass an unrealized loss. As the price goes up, short sellers may be forced to close their positions. This can occur via stop-loss triggers, liquidations (for margin and futures contracts). It can also happen simply because traders manually close their positions to avoid even greater losses.
So, how do short sellers close their positions? They buy. This is why a short squeeze results in a sharp price spike. As short sellers close their positions, a cascading effect of buy orders adds more fuel to the fire. As such, a short squeeze is typically accompanied by an equivalent spike in trading volume.
Here’s something else to consider. The larger the short interest is, the easier it is to trap short sellers and force them to close their positions. In other words, the more liquidity there is to trap, the greater the increase in volatility may be thanks to a short squeeze. In this sense, a short squeeze is a temporary increase in demand while a decrease in supply.
The opposite of a short squeeze is a long squeeze – though it’s less common. A long squeeze is a similar effect that happens when longs get trapped by cascading selling pressure, leading to a sharp downward price spike.
How does a short squeeze happen?
A short squeeze happens when there is a sudden increase in buying pressure. If you’ve read our article about shorting, you know that shorting can be a high-risk strategy. However, what makes a short squeeze a particularly volatile event is the sudden rush to quickly cover short positions (via buy orders). This includes many stop-loss orders triggering at a significant price level, and many short sellers manually closing their positions at the same time.
A short squeeze can happen in essentially any financial market where a short position can be taken. At the same time, the lack of options to short a market can also lead to large price bubbles. After all, if there’s no good way to bet against an asset, it may keep going up for an extended period.
A prerequisite of a short squeeze can be a majority of short positions over long positions. Naturally, if there are significantly more short positions than long positions, there’s more liquidity available to fuel the fire. This is why the long/short ratio can be a useful tool for traders who want to keep an eye on market sentiment. If you’d like to check the real-time long/short ratio for Binance Futures, you can do it on this page.
Some advanced traders will look for potential short squeeze opportunities to go long and profit off the quick spike in price. This strategy will include accumulating a position before the squeeze happens and using the quick spike to sell at a higher price.
Short squeeze examples
Short squeezes are very common in the stock market. This usually entails low sentiment around a company, a perceived high stock price, and a large number of short positions. If, say, some unexpected positive news comes out, all those short positions are forced to buy, leading to an increase in the price of the stock. Even so, a short squeeze is more of a technical pattern rather than a fundamental event.
According to some estimates, Tesla (TSLA) stock had been one of the most shorted stocks in history. Even so, the price has gone through a number of sharp rises, likely trapping a lot of short sellers.
Short squeezes are also quite common in the cryptocurrency markets, most notably in the Bitcoin markets. The Bitcoin derivatives market uses high-leverage positions, and these can be trapped or liquidated with relatively small price moves. As such, short and long squeezes happen frequently in the Bitcoin markets. If you’d like to avoid getting liquidated or trapped in such moves, carefully consider the amount of leverage you’re using. You should also adopt a proper risk management strategy.
Take a look at this Bitcoin price range below from early 2019. The price was contained in a range after a sharp move to the downside. Market sentiment was likely quite low, as many investors would be looking for short positions, expecting the continuation of the downtrend.
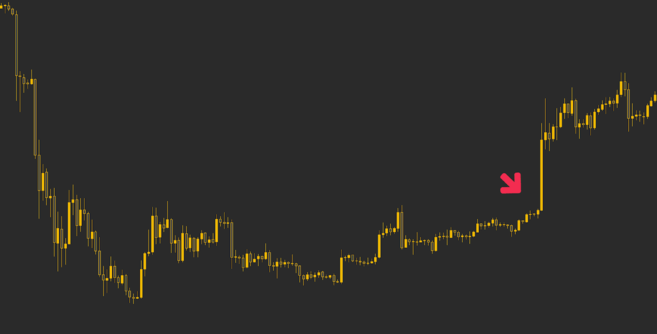
Potential short squeeze on the BTC/USD market.
However, price flew through the range with such haste that the area didn’t even get retested for a long time. It only got a retest years later, during the coronavirus pandemic (also known as “Black Thursday”). This rapid move was quite likely due to extensive short covering.
Closing thoughts
Summing up, a short squeeze happens when short sellers get trapped and are forced to cover their positions, leading to a sharp price increase.
Short squeezes can be especially volatile in highly levered markets. When many traders and investors use high leverage, the price moves also tend to be sharper, since cascading liquidations can lead to a waterfall effect.
Make sure you understand the implications of a short squeeze before you enter a short position. Otherwise, you could end up with huge losses.




